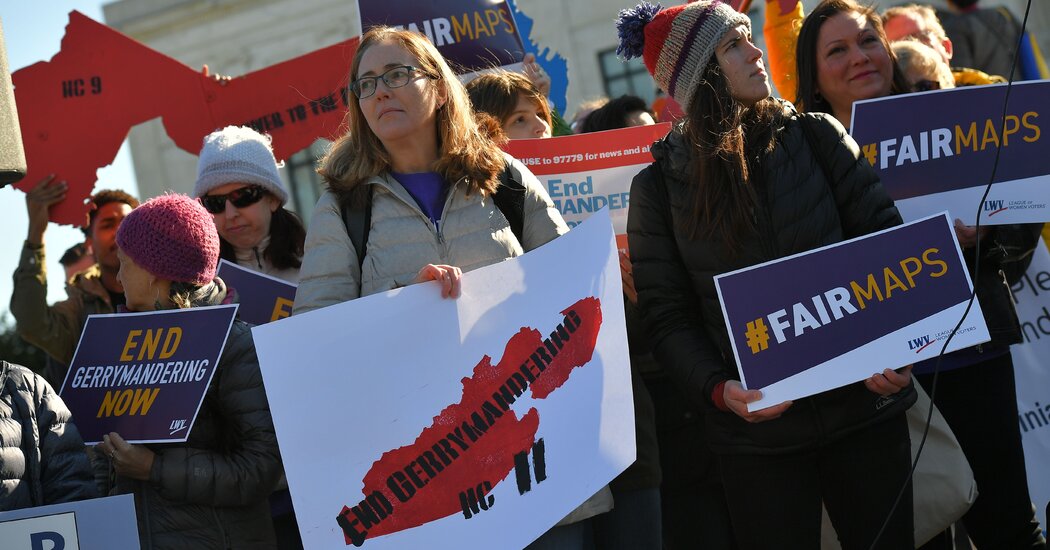
The Supreme Court on Monday allowed congressional maps that had been approved by state courts in North Carolina and Pennsylvania to stand, giving Democrats an advantage in this year’s election in two key states.
In issuing the orders, the Supreme Court rejected requests by Republicans to restore maps approved by G.O.P.-controlled state legislatures. Those district lines were thrown out and replaced by courts in both states after challenges by Democrats.
Under the new court-imposed maps in both states, Democrats are likely to gain more seats than they would have under the legislature-approved versions.
But in the North Carolina case, there were signs that at least four of the court’s more conservative justices could later rule that state courts are powerless to change congressional maps adopted by state legislatures.
Advertisement
Continue reading the main story
Such a ruling would fundamentally alter how congressional elections are conducted and amplify partisan gerrymandering, allowing the party that controls the legislature to draw voting districts favoring its candidates.
But that will not happen before this fall’s election.
Stanton Jones, a lawyer for some of the plaintiffs who had challenged the North Carolina map, said the Supreme Court’s order meant that “North Carolina voters will now be able to vote in free and fair congressional elections this year.”
He said that for now, the order signaled an end to “a decade of extreme Republican gerrymanders.”
Still, the court’s three most conservative members — Justices Samuel A. Alito Jr., Clarence Thomas and Neil M. Gorsuch — said they would have blocked the North Carolina map because it was likely that the State Supreme Court had violated the Constitution in overriding the State Legislature.
Taken together, the two opinions suggested that there are four justices ready to add a case on the question to the court’s docket when it is next presented in a petition seeking the court’s review rather than on what critics call the court’s shadow docket. It takes four votes to grant such review.
But it takes five votes to prevail. The swing vote would almost certainly belong to Justice Amy Coney Barrett.
In a second order in the Pennsylvania case, the court provisionally turned down a similar application on technical grounds without noted dissent.
The North Carolina Supreme Court had rejected a map drawn by Republican lawmakers that effectively gave their party at least 10 of the state’s 14 House seats, notwithstanding that voters statewide are roughly equally divided between the two parties.
A three-judge panel of the state Superior Court in Raleigh instead adopted a new map drawn by a nonpartisan panel of redistricting experts that appeared to split North Carolina’s congressional districts roughly equally between Republicans and Democrats. It gave each party six relatively safe House seats and made the other two competitive.
After the State Supreme Court refused to block that ruling, Republican state officials asked the U.S. Supreme Court to step in.
In the Pennsylvania case, the State Supreme Court adopted a map that appears to give Republicans nine fairly safe seats and Democrats eight, according to an analysis by the nonpartisan Campaign Legal Center. Each party currently holds nine House seats, but Pennsylvania will lose a seat next year because of reapportionment after the 2020 census.
Advertisement
Continue reading the main story
Voters and a Republican candidate for the House sued state officials in federal court to challenge the new map. When they did not receive immediate relief, they asked the U.S. Supreme Court to intervene.
Both emergency applications relied on the Elections Clause of the Constitution, which says “the times, places and manner of holding elections for senators and representatives, shall be prescribed in each state by the legislature thereof.” That meant, the challengers argued, that the state legislature has sole responsibility for drawing congressional districts and that state courts have no role to play.
“The question presented here,” North Carolina Republicans wrote in their application, “goes to the very core of this nation’s democratic republic: what entity has the constitutional authority to set the rules of the road for federal elections.”
In issuing the orders, the Supreme Court rejected requests by Republicans to restore maps approved by G.O.P.-controlled state legislatures. Those district lines were thrown out and replaced by courts in both states after challenges by Democrats.
Under the new court-imposed maps in both states, Democrats are likely to gain more seats than they would have under the legislature-approved versions.
But in the North Carolina case, there were signs that at least four of the court’s more conservative justices could later rule that state courts are powerless to change congressional maps adopted by state legislatures.
Advertisement
Continue reading the main story
Such a ruling would fundamentally alter how congressional elections are conducted and amplify partisan gerrymandering, allowing the party that controls the legislature to draw voting districts favoring its candidates.
But that will not happen before this fall’s election.
Stanton Jones, a lawyer for some of the plaintiffs who had challenged the North Carolina map, said the Supreme Court’s order meant that “North Carolina voters will now be able to vote in free and fair congressional elections this year.”
He said that for now, the order signaled an end to “a decade of extreme Republican gerrymanders.”
Still, the court’s three most conservative members — Justices Samuel A. Alito Jr., Clarence Thomas and Neil M. Gorsuch — said they would have blocked the North Carolina map because it was likely that the State Supreme Court had violated the Constitution in overriding the State Legislature.

Supreme Court Allows Court-Imposed Voting Maps in North Carolina and Pennsylvania
State courts had ruled that earlier maps for congressional elections had been warped by partisan gerrymandering. Democrats stand to benefit from the justices’ decision.
 www.nytimes.com
www.nytimes.com

Supreme Court Allows Court-Imposed Voting Maps in North Carolina and Pennsylvania
State courts had ruled that earlier maps for congressional elections had been warped by partisan gerrymandering. Democrats stand to benefit from the justices’ decision.
Taken together, the two opinions suggested that there are four justices ready to add a case on the question to the court’s docket when it is next presented in a petition seeking the court’s review rather than on what critics call the court’s shadow docket. It takes four votes to grant such review.
But it takes five votes to prevail. The swing vote would almost certainly belong to Justice Amy Coney Barrett.
In a second order in the Pennsylvania case, the court provisionally turned down a similar application on technical grounds without noted dissent.
The North Carolina Supreme Court had rejected a map drawn by Republican lawmakers that effectively gave their party at least 10 of the state’s 14 House seats, notwithstanding that voters statewide are roughly equally divided between the two parties.
A three-judge panel of the state Superior Court in Raleigh instead adopted a new map drawn by a nonpartisan panel of redistricting experts that appeared to split North Carolina’s congressional districts roughly equally between Republicans and Democrats. It gave each party six relatively safe House seats and made the other two competitive.
After the State Supreme Court refused to block that ruling, Republican state officials asked the U.S. Supreme Court to step in.
In the Pennsylvania case, the State Supreme Court adopted a map that appears to give Republicans nine fairly safe seats and Democrats eight, according to an analysis by the nonpartisan Campaign Legal Center. Each party currently holds nine House seats, but Pennsylvania will lose a seat next year because of reapportionment after the 2020 census.
Advertisement
Continue reading the main story
Voters and a Republican candidate for the House sued state officials in federal court to challenge the new map. When they did not receive immediate relief, they asked the U.S. Supreme Court to intervene.
Both emergency applications relied on the Elections Clause of the Constitution, which says “the times, places and manner of holding elections for senators and representatives, shall be prescribed in each state by the legislature thereof.” That meant, the challengers argued, that the state legislature has sole responsibility for drawing congressional districts and that state courts have no role to play.
“The question presented here,” North Carolina Republicans wrote in their application, “goes to the very core of this nation’s democratic republic: what entity has the constitutional authority to set the rules of the road for federal elections.”

