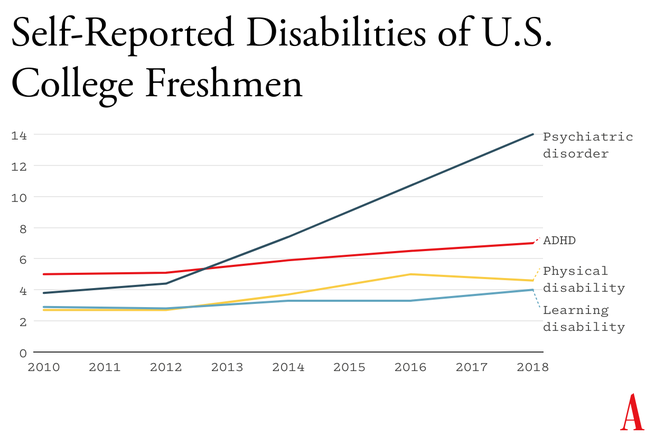
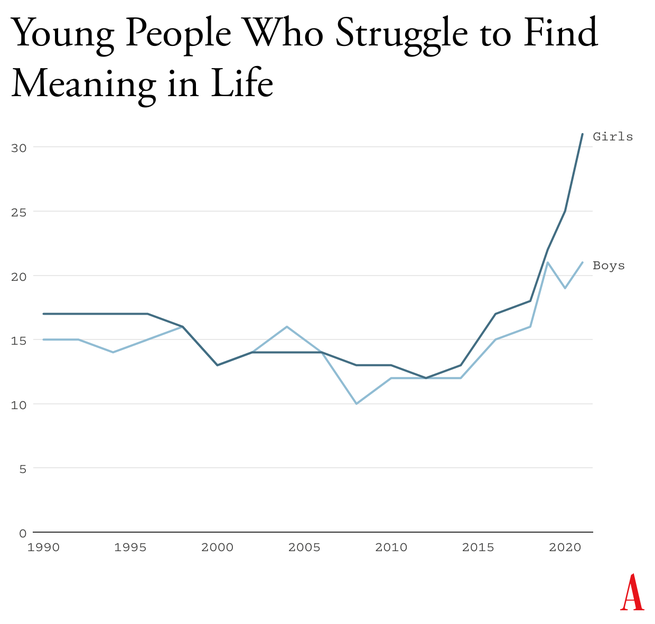
Haidt's stuff is always at least thought provoking. . . not sure the exact harm phones/social media are producing, but interesting to watch the research and debate roll in.
The environment in which kids grow up today is hostile to human development.
By Jonathan Haidt
Photographs by Maggie Shannon
Something went suddenly and horribly wrong for adolescents in the early 2010s. By now you’ve likely seen the statistics: Rates of depression and anxiety in the United States—fairly stable in the 2000s—rose by more than 50 percent in many studies from 2010 to 2019. The suicide rate rose 48 percent for adolescents ages 10 to 19. For girls ages 10 to 14, it rose 131 percent.
The problem was not limited to the U.S.: Similar patterns emerged around the same time in Canada, the U.K., Australia, New Zealand, the Nordic countries, and beyond. By a variety of measures and in a variety of countries, the members of Generation Z (born in and after 1996) are suffering from anxiety, depression, self-harm, and related disorders at levels higher than any other generation for which we have data.
The decline in mental health is just one of many signs that something went awry. Loneliness and friendlessness among American teens began to surge around 2012. Academic achievement went down, too. According to “The Nation’s Report Card,” scores in reading and math began to decline for U.S. students after 2012, reversing decades of slow but generally steady increase. PISA, the major international measure of educational trends, shows that declines in math, reading, and science happened globally, also beginning in the early 2010s.
Read: It sure looks like phones are making students dumber
As the oldest members of Gen Z reach their late 20s, their troubles are carrying over into adulthood. Young adults are dating less, having less sex, and showing less interest in ever having children than prior generations. They are more likely to live with their parents. They were less likely to get jobs as teens, and managers say they are harder to work with. Many of these trends began with earlier generations, but most of them accelerated with Gen Z.
Surveys show that members of Gen Z are shyer and more risk averse than previous generations, too, and risk aversion may make them less ambitious. In an interview last May, OpenAI co-founder Sam Altman and Stripe co-founder Patrick Collison noted that, for the first time since the 1970s, none of Silicon Valley’s preeminent entrepreneurs are under 30. “Something has really gone wrong,” Altman said. In a famously young industry, he was baffled by the sudden absence of great founders in their 20s.
Generations are not monolithic, of course. Many young people are flourishing. Taken as a whole, however, Gen Z is in poor mental health and is lagging behind previous generations on many important metrics. And if a generation is doing poorly––if it is more anxious and depressed and is starting families, careers, and important companies at a substantially lower rate than previous generations––then the sociological and economic consequences will be profound for the entire society.
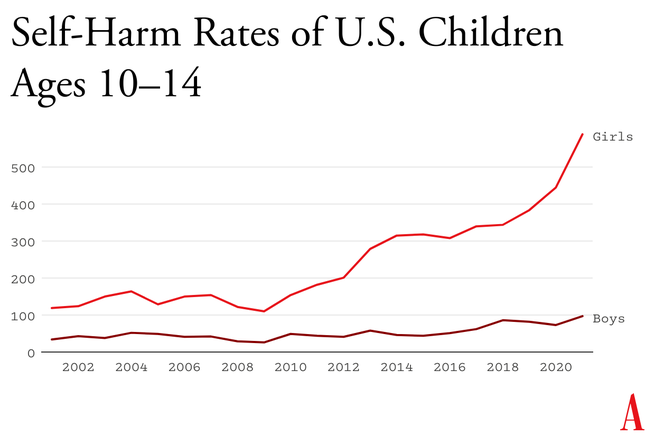 Number of emergency-department visits for nonfatal self-harm per 100,000 children (source: Centers for Disease Control and Prevention)
Number of emergency-department visits for nonfatal self-harm per 100,000 children (source: Centers for Disease Control and Prevention)
What happened in the early 2010s that altered adolescent development and worsened mental health? Theories abound, but the fact that similar trends are found in many countries worldwide means that events and trends that are specific to the United States cannot be the main story.
I think the answer can be stated simply, although the underlying psychology is complex: Those were the years when adolescents in rich countries traded in their flip phones for smartphones and moved much more of their social lives online—particularly onto social-media platforms designed for virality and addiction. Once young people began carrying the entire internet in their pockets, available to them day and night, it altered their daily experiences and developmental pathways across the board. Friendship, dating, sexuality, exercise, sleep, academics, politics, family dynamics, identity—all were affected. Life changed rapidly for younger children, too, as they began to get access to their parents’ smartphones and, later, got their own iPads, laptops, and even smartphones during elementary school.
Jonathan Haidt: Get phones out of schools now
As a social psychologist who has long studied social and moral development, I have been involved in debates about the effects of digital technology for years. Typically, the scientific questions have been framed somewhat narrowly, to make them easier to address with data. For example, do adolescents who consume more social media have higher levels of depression? Does using a smartphone just before bedtime interfere with sleep? The answer to these questions is usually found to be yes, although the size of the relationship is often statistically small, which has led some researchers to conclude that these new technologies are not responsible for the gigantic increases in mental illness that began in the early 2010s.
But before we can evaluate the evidence on any one potential avenue of harm, we need to step back and ask a broader question: What is childhood––including adolescence––and how did it change when smartphones moved to the center of it? If we take a more holistic view of what childhood is and what young children, tweens, and teens need to do to mature into competent adults, the picture becomes much clearer. Smartphone-based life, it turns out, alters or interferes with a great number of developmental processes.
The intrusion of smartphones and social media are not the only changes that have deformed childhood. There’s an important backstory, beginning as long ago as the 1980s, when we started systematically depriving children and adolescents of freedom, unsupervised play, responsibility, and opportunities for risk taking, all of which promote competence, maturity, and mental health. But the change in childhood accelerated in the early 2010s, when an already independence-deprived generation was lured into a new virtual universe that seemed safe to parents but in fact is more dangerous, in many respects, than the physical world.
My claim is that the new phone-based childhood that took shape roughly 12 years ago is making young people sick and blocking their progress to flourishing in adulthood. We need a dramatic cultural correction, and we need it now.
The environment in which kids grow up today is hostile to human development.
By Jonathan Haidt
Photographs by Maggie Shannon
Something went suddenly and horribly wrong for adolescents in the early 2010s. By now you’ve likely seen the statistics: Rates of depression and anxiety in the United States—fairly stable in the 2000s—rose by more than 50 percent in many studies from 2010 to 2019. The suicide rate rose 48 percent for adolescents ages 10 to 19. For girls ages 10 to 14, it rose 131 percent.
The problem was not limited to the U.S.: Similar patterns emerged around the same time in Canada, the U.K., Australia, New Zealand, the Nordic countries, and beyond. By a variety of measures and in a variety of countries, the members of Generation Z (born in and after 1996) are suffering from anxiety, depression, self-harm, and related disorders at levels higher than any other generation for which we have data.
The decline in mental health is just one of many signs that something went awry. Loneliness and friendlessness among American teens began to surge around 2012. Academic achievement went down, too. According to “The Nation’s Report Card,” scores in reading and math began to decline for U.S. students after 2012, reversing decades of slow but generally steady increase. PISA, the major international measure of educational trends, shows that declines in math, reading, and science happened globally, also beginning in the early 2010s.
Read: It sure looks like phones are making students dumber
As the oldest members of Gen Z reach their late 20s, their troubles are carrying over into adulthood. Young adults are dating less, having less sex, and showing less interest in ever having children than prior generations. They are more likely to live with their parents. They were less likely to get jobs as teens, and managers say they are harder to work with. Many of these trends began with earlier generations, but most of them accelerated with Gen Z.
Surveys show that members of Gen Z are shyer and more risk averse than previous generations, too, and risk aversion may make them less ambitious. In an interview last May, OpenAI co-founder Sam Altman and Stripe co-founder Patrick Collison noted that, for the first time since the 1970s, none of Silicon Valley’s preeminent entrepreneurs are under 30. “Something has really gone wrong,” Altman said. In a famously young industry, he was baffled by the sudden absence of great founders in their 20s.
Generations are not monolithic, of course. Many young people are flourishing. Taken as a whole, however, Gen Z is in poor mental health and is lagging behind previous generations on many important metrics. And if a generation is doing poorly––if it is more anxious and depressed and is starting families, careers, and important companies at a substantially lower rate than previous generations––then the sociological and economic consequences will be profound for the entire society.

What happened in the early 2010s that altered adolescent development and worsened mental health? Theories abound, but the fact that similar trends are found in many countries worldwide means that events and trends that are specific to the United States cannot be the main story.
I think the answer can be stated simply, although the underlying psychology is complex: Those were the years when adolescents in rich countries traded in their flip phones for smartphones and moved much more of their social lives online—particularly onto social-media platforms designed for virality and addiction. Once young people began carrying the entire internet in their pockets, available to them day and night, it altered their daily experiences and developmental pathways across the board. Friendship, dating, sexuality, exercise, sleep, academics, politics, family dynamics, identity—all were affected. Life changed rapidly for younger children, too, as they began to get access to their parents’ smartphones and, later, got their own iPads, laptops, and even smartphones during elementary school.
Jonathan Haidt: Get phones out of schools now
As a social psychologist who has long studied social and moral development, I have been involved in debates about the effects of digital technology for years. Typically, the scientific questions have been framed somewhat narrowly, to make them easier to address with data. For example, do adolescents who consume more social media have higher levels of depression? Does using a smartphone just before bedtime interfere with sleep? The answer to these questions is usually found to be yes, although the size of the relationship is often statistically small, which has led some researchers to conclude that these new technologies are not responsible for the gigantic increases in mental illness that began in the early 2010s.
But before we can evaluate the evidence on any one potential avenue of harm, we need to step back and ask a broader question: What is childhood––including adolescence––and how did it change when smartphones moved to the center of it? If we take a more holistic view of what childhood is and what young children, tweens, and teens need to do to mature into competent adults, the picture becomes much clearer. Smartphone-based life, it turns out, alters or interferes with a great number of developmental processes.
The intrusion of smartphones and social media are not the only changes that have deformed childhood. There’s an important backstory, beginning as long ago as the 1980s, when we started systematically depriving children and adolescents of freedom, unsupervised play, responsibility, and opportunities for risk taking, all of which promote competence, maturity, and mental health. But the change in childhood accelerated in the early 2010s, when an already independence-deprived generation was lured into a new virtual universe that seemed safe to parents but in fact is more dangerous, in many respects, than the physical world.
My claim is that the new phone-based childhood that took shape roughly 12 years ago is making young people sick and blocking their progress to flourishing in adulthood. We need a dramatic cultural correction, and we need it now.