
By Paul Krugman
Opinion Columnist
You’re reading the Paul Krugman newsletter, for Times subscribers only. A guide to U.S. politics and the economy — from the mainstream to the wonkish. Get it in your inbox.
True story: When I won the Nobel Prize in 2008, Princeton quickly set up a special event on campus and reserved a parking space for me in front of Robertson Hall. But when I drove up in my 2004 Jetta, the security people frantically tried to wave me away. They clearly didn’t find it plausible that a laureate would be driving such a modest car.
I’m still driving that car today.
The point is that I’m not one of those people who cares much about what he drives. (No doubt I act out my egotism in other ways.) But many people do, in fact, use their cars to symbolize their status — indeed, their identity.
There’s no point being censorious. Conspicuous consumption is a very human thing, going back as far as civilization itself. Over time, however, the form has changed. These days it’s relatively hard to tell how rich people are by the clothes they wear, which gives other status markers like cars a more important role. Also, in modern times people use consumer goods to display their values as well as their wealth. A fancy pickup truck sends one kind of message; a Tesla sends another.
And yes, speaking of Tesla, today’s newsletter is partly about Elon Musk.
As I wrote in my last newsletter, the main reason to believe that Tesla’s huge market value doesn’t make sense has little to do with Musk’s antics at Twitter. The problem instead is that Tesla’s dominance of the electric vehicle market is already fading as we speak, so the company is unlikely to generate the kind of extraordinary long-term profits that would justify its stock price.
Advertisement
Continue reading the main story
That said, Musk has indeed been acting very oddly — and in ways that seem almost perfectly calculated to drive away his best customers.
After all, what does it mean to buy a Tesla? It’s a luxury car, but there are other luxury cars. What’s special about a Tesla is that it’s an electric, zero-emission luxury car — one that purports to be a glitzy ride to a sustainable future.
Also, until just the other day, Musk himself was widely seen as a cool guy. And cool in a futuristic sense: His company sends rockets into outer space; he was living with a popular musician who released an album inspired by the science-fiction novel “Dune” (a book that, by the way, was recently made into a terrific movie).
So what message was someone sending by driving a Tesla? Basically — I don’t think I’m being unfair — it was: “I’m rich but I’m woke.” Mock that stance all you like, but it really did increase Tesla sales. And it means that many Tesla buyers are probably also Democrats.
I’m not just guessing here. The other day a friend of mine who writes under the nom de internet Invictus used New York State data to compare county-level political leanings with Tesla registrations. Sure enough, in 2020, counties that voted overwhelmingly for Donald Trump — they do exist, even in New York — purchased far fewer Teslas per capita than those that voted overwhelmingly for Joe Biden.
Advertisement
Continue reading the main story
Charles Gaba, known, among other things, for his documentation of the correlation between political leanings and vaccination status, has replicated these results for several states. Here, for example, is what it looks like in California:
Image
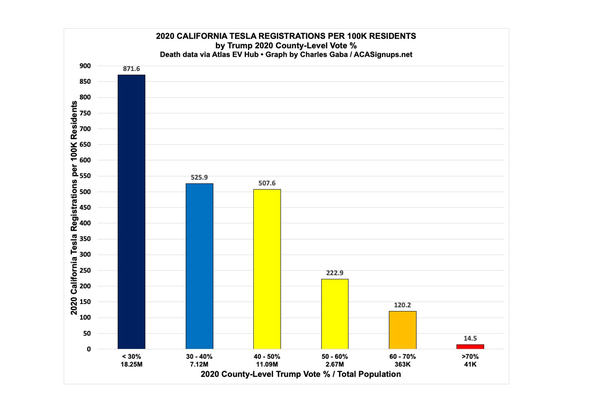
Teslas are a Democratic thing.Credit...Charles Gaba

To delve a bit deeper, here’s a comparison — using data from Invictus and the American Community Survey — between Steuben County, a very Trumpy area southeast of Buffalo, and Westchester County, a wealthy and very Democratic New York suburb that includes Scarsdale:
Image
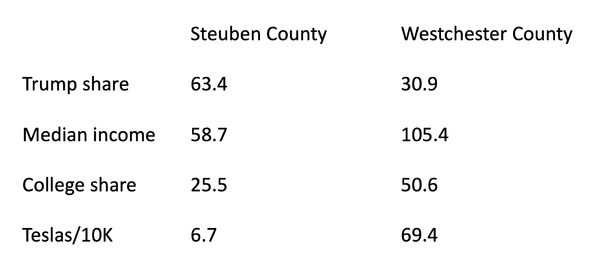
Rich, woke Tesla drivers, New York edition.Credit...Invictus, American Community Survey

So, yes, there are a lot of Teslas in Westchester, hardly any in Steuben. To some extent this may reflect the fact that people in Westchester have more income. But despite what you sometimes hear about the parties reversing class roles lately, Americans with incomes over $100,000 still vote Republican by a fairly large margin. What has reversed is the educational divide: College graduates have become a Democratic bloc, which supports the view that what we might call the Tesla divide is also linked to the culture war. And Westchester has far more college graduates than Steuben does.
Tesla, then, is a brand whose customer base largely consists of wealthy cultural liberals who were attracted in part by Elon Musk’s perceived with-it persona. Given all that, Musk’s public embrace of MAGA conspiracy theories is an almost inconceivably bad marketing move, practically designed to alienate his main buyers. What’s going on?
To a large extent Musk may simply be revealing who he always was — basically, a typical technology oligarch. In general, authoritarian instincts and contempt for the little people are a lot more prevalent among the Silicon Valley elite than people realized when information technology still felt cool.
Even among his class, however, Musk stands out for his lack of impulse control. This was obvious, if you paid attention, long before he bought Twitter. More than four years have passed since he called a cave rescuer who rejected Musk’s offer of a mini-submarine a “pedo guy.”
Furthermore, Musk’s behavior is becoming even more bizarre. (A favorite line of mine is that people get worse as they grow older because they become more like themselves.) Since when do captains of industry respond to random critics by mocking their imagined anatomies?
Now, as I wrote in my last newsletter, Tesla was probably headed for a fall eventually, even if Musk had been who his fans imagined him to be; the economics of the electric vehicle business just aren’t conducive to long-term market domination. But Musk might have been able to postpone the day of reckoning, at least for a while, if he had managed to hide who he was from his best customers a little longer.
