This Georgia County Spent $1 Million to Avoid Paying for One Employee’s Gender-Affirming Care
Officials in Houston County, Georgia, said gender-affirming surgery for sheriff’s deputy Anna Lange was too costly. They spent more than $1 million on private lawyers in a fight to keep transition-related care from being covered by their health plan.
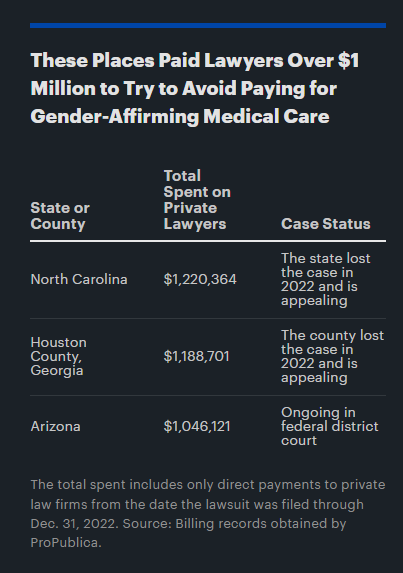
In the years that followed, the central Georgia county paid a private law firm nearly $1.2 million to fight Sgt. Anna Lange in federal court — far more than it would have cost the county to offer such coverage to all of its 1,500 health plan members, according to expert analyses. One expert estimated that including transition-related care in the health plan would add about 0.1% to the cost of all claims, which would come to roughly $10,000 per year, on average.
Since at least 1998, the county's plan has excluded coverage for "services and supplies for a sex change," an outdated term to refer to surgeries or medications related to gender transition. In 2016, the county's insurance administrator recommended changing the policy to align with a new federal nondiscrimination rule. But Houston County leaders said no.
The county argued that even if the cost of expanding its insurance coverage to include transition-related health care was low on average, it could amount to much more in some years. The county also claimed that expanding the plan's coverage would spur demands to pay for other, currently excluded benefits, such as abortion, weight loss surgery and eye surgery.
"It was a slap in the face, really, to find out how much they had spent," said Lange, who filed a federal discrimination lawsuit against the county. "They're treating it like a political issue, obviously, when it's a medical issue."
Major medical associations recognize that access to transition-related care, also known as gender-affirming care, is medically necessary for transgender people, citing evidence that prohibiting it can harm their mental and physical health. And federal judges have consistently ruled that employers cannot categorically exclude gender-affirming care from health care plans, though prior to Lange's suit, there hadn't been a ruling covering Georgia. The care can include long-term hormone therapy, chest and genital surgery, and other services that help transgender people align their bodies with their gender identities.
But banning gender-affirming care has become a touchstone of conservative politics. At least 25 states this year are considering or have passed bills that would ban gender-affirming care for minors. Bills in Oklahoma and Texas aim to ban insurance companies from covering transition-related health care for adults as well.
At the same time, state and local government employers are waging long legal battles against covering gender-affirming care for their employees. With recent estimates showing that 0.6% of all Americans older than 13 are transgender, these employers are spending large sums to fight coverage for a small number of people.
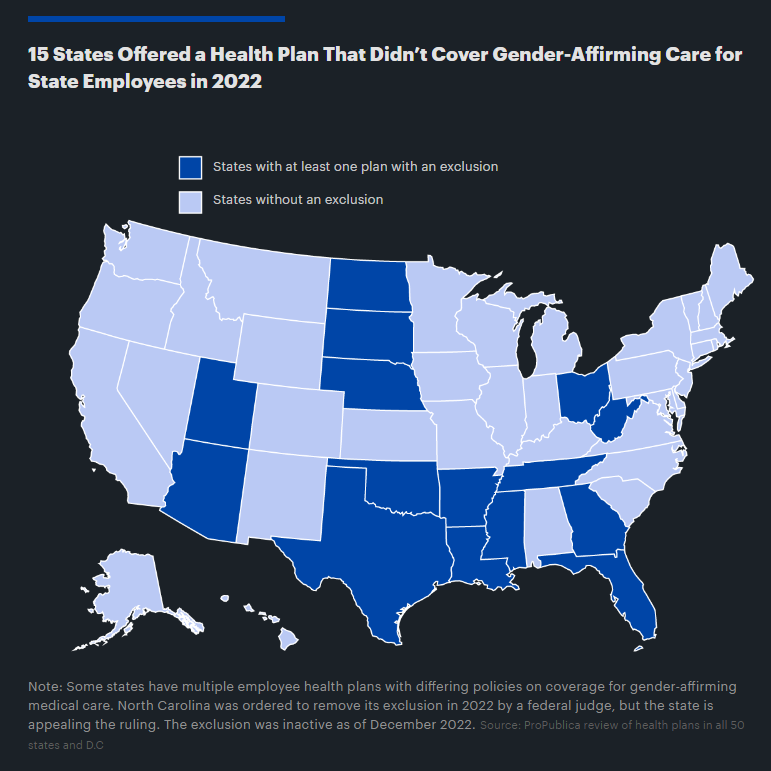
ProPublica obtained records showing that two states — North Carolina and Arizona — have spent more than $1 million in attorney fees on legal fights similar to the one in Houston County. Both have claimed in court filings that the decisions they made not to cover the care for employees are purely financial and not discriminatory.
But budget estimates and real-world examplesshow that the cost of offering coverage of gender-affirming care is negligible. When the state of North Carolina briefly covered gender-affirming care in 2017, the cost amounted to $400,000 — just 0.01% of the health plan's $3.3 billion annual budget.
----------------------
Compared to North Carolina and Arizona, Houston County stands out for the huge legal bill it amassed relative to its small size. North Carolina's employee health plan covers more than 700,000 people and Arizona's covers over 130,000 people, dwarfing Houston County's 1,500. Yet Houston County has spent a similar amount of money on legal fees as those states in a shorter time, according to records ProPublica obtained.
In fact, Houston County's total legal fees on the Lange case have amounted to almost three times its annual physical and mental health budget. "Is this a good use of public money? No," said Joanna Grossman, a law professor at Southern Methodist University who focuses on sex discrimination. "It's fair to say that this is an issue where it's pretty clear they're going to lose."